The Land and People
Geography of Egypt
Climate
Language
Population
Economy
The Land and People
The Arab Republic of Egypt, home of 104 million people that are nearly distributed in between two major communities, urban and rural, mostly concentrated alongside the length of the river Nile, is divided into 27 governorates (provinces) consisting of major cities (like Cairo, Alexandria, Port Said and others with populations of millions), towns (with populations mostly of 20.000 people) and villages (ranging in size between 500- up to 5000 people),
Throughout the recorded history, the beauty of the Egyptian countryside has been regarded as a heavenly gift.
The Nile Valley has been described as a kaleidoscope of changing colours with different crops, flowers and fruits ripening or blossoming almost monthly. Where green fields have just been harvested the rich, black earth (which gave Egypt its name KEMET in antiquities) offers a sharp contrast with the arid deserts (deshret, meaning the red land in ancient Egypt) on either side of the Nile Valley.
In the Western Desert where sand dunes, rock-strewn tracts and barren hills produce an almost lunar landscape, several oases such as Bahariyya, Farafra, Dakhla, Kharga and Siwa have been inhabited since time immemorial.
In the Eastern Desert and the Sinai, there are some wells and no oases, but the mountainous terrain is rich in minerals, including hard building rocks, semi-precious stones, copper and gold.
Today, thanks to modern techniques and human efforts, large areas of the deserts in Egypt are well turned into green, productive farmland, criss-crossed by irrigation ditches.
Like their culture which combines in a single heritage the successive influence of diverse civilizations, so the Egyptians reflect within their present homogeneity the 5000 years of history of which they are the invisible product.
From Sinouhi of the 12th Dynasty (some 4000 years ago) to the modern Egyptian of 2022, they share of having the same deeply-rooted ties to their birthplace, whatever the distances of place and time; they want finally to return back homeland to their places of origin, for the rest of their lives.
On the other hand, if there’s one characteristic that links the majority of the Egyptians it is an immense pride in, simply being an Egyptian, and proudly tell you, I’M descendant of the ancient Egyptians.
In one way or another, religion (Islam as the religion of the majority) cushions life’s blows. Islam permeates Egyptian life, but manifested not in a strictly way like other Islamic countries – Egyptians love enjoying themselves too much for that – but it’s there at an almost subconscious level. Laughter prevails the social exchange and one of the most enjoyable aspect of travel in Egypt is how much can be negotiated with a smile. But in general the society is a traditional more conservatism in rural areas, where women wear in long, wide black dress called ABBAYA, covering all the body and men wear a gown-like GALLABIYYA, while in urban areas and major cities, especially Cairo and Alexandria, people dress in western style particularly young generations. All, whether in a rural or urban area, are welcoming people
Egypt
Country Name
Official long form: Arab Republic of Egypt
Short form: Egypt
Local long form: Jumhuriyyat Misr IL Arabiyah.
Local Short: Misr (actually pronounced Masr
The President
With great celebrations, hoping that he would bring stability and prosperity to the people of Egypt, Former-Retired-Field-Marshal Abdel Fattah IL Sisi was elected president in May 2014, to become Egypt’s Tenth President.
He served in the Army till the position of Field Marshal, President IL Sisi won a second four-year term in 2018 against a sole candidate, after the two other candidates withdrew from the race.
President IL Sisi in addition to Egypt’s struggling Economy, also struggling against figures of corruption and Extremism
Presidents of Egypt Since 1952 Reolution
| Years | Name |
| 1953-54 | Mohamed Nagueib |
| 1954-1956 | Nasser in Power/not yet President |
| 1956-1970 | Gamal Abdel Nasser |
| 1970-1981 | Anwar Sadat |
| Short interim Period | Soufi Abu Taleb (P.P.A) |
| 1981-2011 | Hosni Mubarak |
| 2012-2013 | Mohamed Morsi |
| 2013-2013 | Adly Mansour (P.S.C.C) |
| 2014 – | Abdel Fattah IL Sisi |
Government
Government Type: Republic.
Capital: Cairo (in process a New one to be Opened following the standard of Upscale Modern Capital, till now name is given (N.A.C – New Administrative Capital).
Independence Day: 28 February 1922 (From UK-)
National Day (Holiday): Revolution day 23 July 1952.
Chief of the State: President Abdel Fattah IL Sisi. (2014-)
Legislative branch: Bicameral System (AL-Nowab “Deputies;” and AL-Shiyoukh “Senators).
Prime Minister: Dr. Moustafa Madbouli.
Judicial branch: Supreme Constitutional Court
Geography of Egypt
Time Zone
Egypt is 2 hours ahead of GMT.
Quick Facts
| Location: | Northern Africa, bordering the Mediterranean Sea, between Libya and the Gaza Strip, and the Red Sea north of Sudan, and includes the Asian Sinai Peninsula |
| Coordinates: | 27 00 N, 30 00 E |
| Area: | total: 1,001,450 sq km land: 995,450 sq km water: 6,000 sq km |
| Area comparative: | slightly more than three times the size of New Mexico, two times the size of France. |
| Land boundaries: | total: 2,665 km border countries: Gaza Strip 11 km, Israel 266 km, Libya 1,115 km, Sudan 1,273 km |
| Coastline: | 2,450 km |
| Maritime claims: | contiguous zone: 24 NM territorial sea: 12 NM continental shelf: 200-m depth or to the depth of exploitation exclusive economic zone: 200 NM |
| Climate: | desert; hot, dry summers with moderate winters |
| Terrain: | vast desert plateau interrupted by Nile valley and delta |
| Elevation extremes: | lowest point: Qattara Depression -133 m highest point: Mount Catherine 2,629 m |
| Natural resources: | petroleum, natural gas, iron ore, phosphates, manganese, limestone, gypsum, talc, asbestos, lead, zinc |
| Geography – note: | controls Sinai Peninsula, only land bridge between Africa and remainder of Eastern Hemisphere; controls Suez Canal, a sea link between Indian Ocean and Mediterranean Sea; size, and juxtaposition to Israel, establish its major role in Middle Eastern geopolitics; dependence on upstream neighbors; dominance of Nile basin issues; prone to influxes of refugees |
Physical Size and Borders
Long known for its ancient civilization that lasted more than three thousand years of human achievements, Egypt a transcontinental country situated in northeastern Africa and with the Sinai Peninsula in Western Asia/Middle East Region.
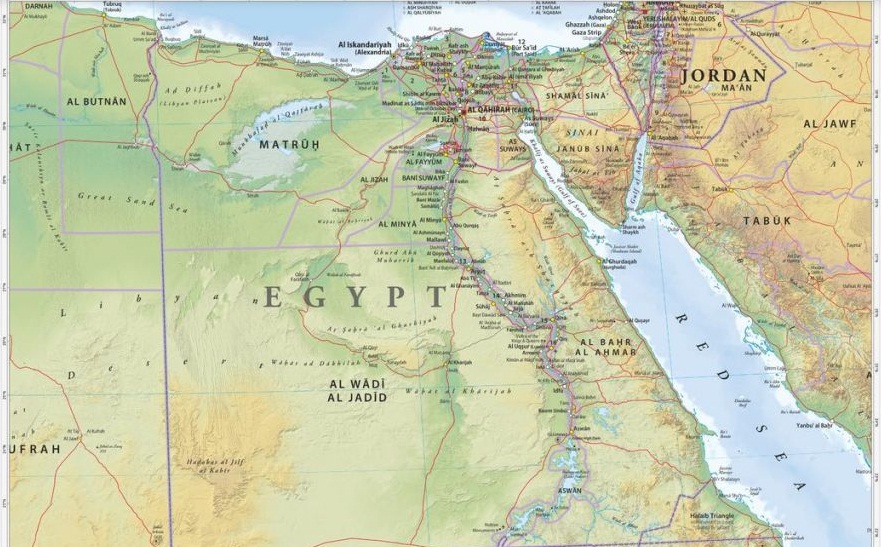
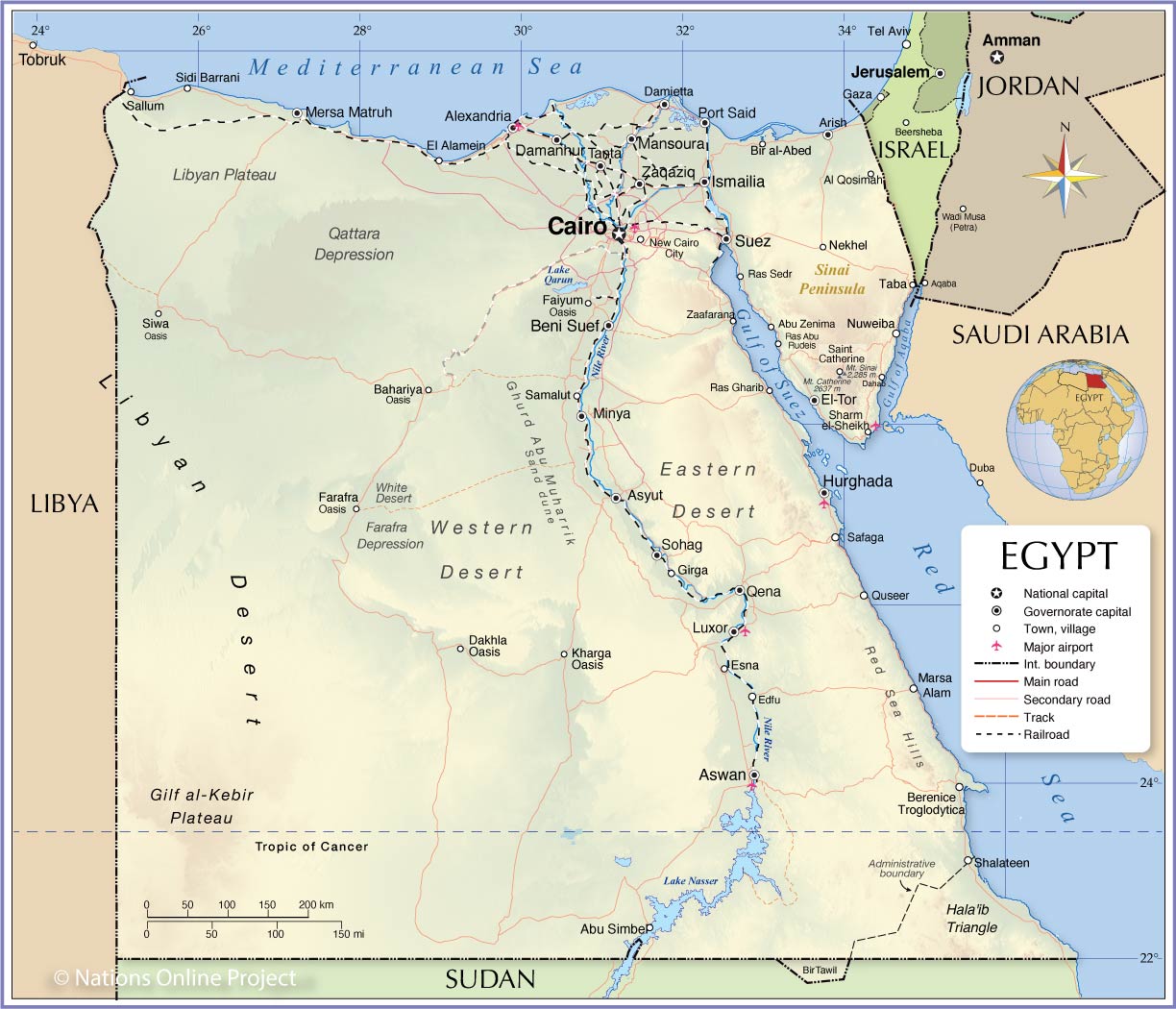
Of what you really see on a map of Egypt, and of political fact, The Arab Republic of Egypt, is a country, bordering the Mediterranean Sea to the north and the Gulf of Suez and the Red Sea to the east, (and as land borders) It is bordered by Libya in the west, the Palestinian territory (Gaza Strip) and Israel in the northeast, and the Sudan in the south. The country’s greatest distance from north to south is 1,024 kilometers, and from east to west, 1,240 kilometers. Egypt’s natural boundaries consist of more than 2,900 kilometers of coastline along the Mediterranean Sea, the Gulf of Suez, the Gulf of Aqaba, and the Red Sea. Egypt shares maritime borders with Cyprus, Greece and Turkey in The Mediterranean Sea, and with Jordan and Saudi Arabia in the Red Sea. , but Geography and Climate of Egypt can be little confusing, for example, while it’s cold and hit by heavy showers in Alexandria, it can be extremely hot and dry in Luxor, but in general; Egypt’ weather is dry cold in winter and hot at the summer days with several days of dusty wind (in the so-called spring). Egyptian Lands are between latitudes 22° – 36° north, which means that the orbit of the cancer goes through the southern part of the country by the city of Aswan, and between latitudes 24°- 37° east of Greenwich. 1,002,000 square kilometers is the total land area but the inhabited area is only 78,990 km2.
Administratively. Egypt is divided into 27 Governorates (in Arabic Muhafza- plural Muhafazat). The Governorates and their capital cities (in brackets) are in Alphabetical order:
Alexandria – (Alexandria).
Aswan – (Aswan).
Asyut – (Asyut).
Beheira – (Damanhur).
Beni Suef (Bani Suwayf).
Cairo – (Cairo).
Dakahlia – (Mansura).
Damietta – (Damietta/Domiyat).
Faiyoum – (EL-Faiyoum).
Gharbiya – (Tanta).
Giza – (EL-Giza).
Ismailiyah – (EL-Ismailiya).
Kafr IL- Sheikh – (Kafr IL-Sheikh).
Luxor – (AL-Uqsur).
Mersa Matrouh – (Matrouh).
Minya – (IL-Miniya).
Monoufiyah/IL-Mnoufiya – (Shibin IL-Koum).
New Valley/ IL-Wady IL-Gediid – (IL-Kharga).
North Sinai/ Shamal Sina – (IL-Arish).
Port Said – (Port Said).
Qaliyoubiyah/IL-Qaliyoubiah – (Banha).
Qena – (Qena).
Red Sea/ IL Bahr IL Ahmar – (IL-Ghardakah/Hurghada).
Sharqiyah/IL-Sharkiayah – (IL-Zaqaziq)
Souhag – (Sohag).
South Sinai/ Ganoub Sina – (IL-Tor).
Suways/Suez – (IL-Suwyas/Suez).
Egypt’ Physical Figure- Natural Regions
The Nile Valley and Delta
The Nile Valley and Delta, which is considered the most extensive oasis on earth, was created by the world’s second-longest river and its seemingly unfailing source. Without a fabled blessed River (The Nile) Egypt would be entirely desert; the Nile River traverses about 1,600 kilometers through Egypt and flows northward from the Egyptian-Sudanese border in the very south to the Mediterranean Sea in the very north, but in fact The Nile is a combination of three long rivers whose sources are in central Africa: the White Nile, the Blue Nile, and the Atbarah.
The Nile enters Egypt a few kilometers north of Wadi Halfa (a Sudanese town), as a result of the High Dam’s construction, which created behind (the largest man-made Lake in the world of 500 KM long) the Nile actually begins its flow into Egypt as Lake Nasser, from Aswan to Cairo the Nile flows in between two plateaus, created a fertile valley on its two banks, was home of a kingdom (Upper Egypt), before it was united with its northern counterpart around 3200 BC.
North of Cairo by some 40 KM, the Nile spreads out over what was once a broad estuary that has been filled by silt deposits to form a fertile, fan-shaped delta about 250 kilometers wide at the seaward base and about 160 kilometers from north to south. The Nile Delta extends over approximately 22,000 square kilometers is considered (together with the Fayoum Region) the most fertile land in the whole country.
The Red Land
There are two main deserts in Egypt, the eastern desert and the western desert.
The Western Desert
The Western Desert covers three quarters/or two thirds of the total area of Egypt i.e 710,000 sq.kms. It is formed by a series of plateaus, the three principal ones being separated by depressions in which-beginning from the south- lie the oases of IL-Kharga, IL-Dakhla, Farafra, IL-Bahariya and Siwa. South of the North-Coast at IL-Alamein lies the Qattarah Depression, which, is one of the largest of its kind in the world. Surrounded by high banks to the north and west, it is open to the east and south where it gradually slopes up to the level of the desert. It has an area of 19,500 sq.kms (about 4.6 million Feddans/Acres, which exceeds that of the Nile Delta by nearly one million Feddan/Acre.
The Eastern Desert
The Eastern Desert is covering an area of 222.000 SQ.KMS, Stretches from the Valley of the Nile to the Red Sea and the Gulf of Suez. It contains a chain of mountains, some of which reach an altitude of over 2.000 meters, extending to the borders of the Red Sea, from which they are separated only by a narrow strip of hills. Rainfall is even lower than in Sinai, below 100mm throughout. There are no permanent water courses, though water is retained over the harder rock, appearing at the surface as springs. There is little cultivation, due to the aridity, though there are settlements on the Red Sea Coast and around the mineral workings, which include petrol, Phosphates, manganese and large deposits of Iron.
Sinai Peninsula
This triangular area covers about 62,000 square kilometers (slightly smaller than West Virginia). Similar to the desert, the peninsula contains mountains in its southern sector that are a geological extension of the Red Sea Hills, the low range along the Red Sea coast that includes Mount Catherine (Jabal Katrinah), the country’s highest point–2,642 meters. The Red Sea is named after these mountains, which are red.
The southern side of the peninsula has escarpment that slides sharply into a narrow coastal ridge that slopes into the Red Sea and the Gulf of Aqaba. The elevation of Sinai’s southern mountainous edge is about 1,000 meters. Moving northward, the elevation of this limestone plateau decreases. The northern third of Sinai is a flat, sandy coastal plain, which extends from the Suez Canal into the Gaza Strip and Israel.
Since 1982 the peninsula, administratively divide into two governorates. North Sinai (its capital is Al Arish city) and the South Sinai ( its capital is At Tur).
Statistics-source: World Fact.
Climate
N.B:
Please note that the hereunder description of Egypt’ Climate is in general and indicative, but you may find some changes in weather nowadays, due to global climate change. It’s highly advised that before your arrival, to be into weather forecast news, (your Dima Travel Consultant/Tour Operator, will send you a printable weather forecast, covering your holiday in Egypt).
If you want to know how weather actually looks like in Egypt, in two words, it is said like that, Egypt has only two seasons: a mild winter from November to April and a hot summer from May to October. Or in another way, Throughout Egypt, days are commonly warm or hot, and nights are cool.
The only differences between the seasons are variations in daytime temperatures and changes in prevailing winds. For instance, in the coastal regions overlooking the Mediterranean Sea, temperatures range between an average minimum of 14 C in winter and an average maximum of 30 C in summer. But temperatures vary widely in the inland desert areas, especially in summer, when they may range from 12-15 C at night to 40 C during the day. During winter, temperatures in the desert fluctuate less dramatically, but they can be as low as 0 C at night and as high as 18 C during the day.
In the north, the cooler temperatures of Alexandria during the summer have made the cities like Alexandria, Mersa Matrouh, Port Said, etc popular summer-destinations resorts especially Alexandria.
But moving southwards from The Nile Delta to Abu Simbel, The average annual temperature increases.. Throughout the Delta and the northern Nile Valley, there are occasional winter cold spells accompanied by light frost and/sometimes even snow. At Aswan, in the south, June temperatures can be as low as 22-25 C at night and as high as 41-45 C during the day when the sky is clear.
Rain and Season:
In general, nationwide, Egypt receives fewer than eighty millimeters of precipitation annually in most areas. Most rain falls along the coast/ mainly the northern coast, but even the wettest area, around Alexandria, receives only about 200 millimeters of precipitation per year. Alexandria has relatively high humidity, but the sea breezes help keep the moisture down to a comfortable level. As moving southward, the amount decreases suddenly. Cairo receives a little more than one centimeter of precipitation each year. The city, however, reports humidity as high as 77 percent during the summer. But during the rest of the year, humidity is low. Cities south of Cairo receive only traces of rainfall. Some areas will go years without rain and then experience sudden downpours that result in flash floods. The Sinai Area in the general receives somewhat more rainfall than the other desert areas.
The Phenomena
A phenomenon of Egypt’s climate is that, its hot spring wind that blows across the country. These winds are known to Europeans as the sirocco but to the Egyptians it is known as the khamsin (literally 50- as throughout the year covering 50 days) , usually arrive in April but occasionally occur in March and May. The winds form in small but vigorous low-pressure areas in the Isthmus of Suez and sweep across the northern coast of Africa. Unobstructed by geographical features, the winds reach high velocities and carry great quantities of sand and dust from the deserts. These sandstorms, often accompanied by winds of up to 140 kilometers per hour, can cause temperatures to rise as much as 20 C in two hours. The winds blow intermittently and may continue for days.
N.B:
Just be careful on hot days especially in summer. If you want to see sites during hot days, either go early in the morning or late in the day (Most Archaeological Sites in Upper Egypt open very early in the morning and close in the evening). And don’t forget to enjoy a stroll along the Nile in the evening as there will be a cool breeze and lots of people watching going on or try a felucca ride.
Official Language in Egypt
Arabic is the official language, though most people understand English and some highly educated people do speak French, in less percentage German, Spanish and Italian, while in the field of tourism, you’ll find many who speak almost all known languages.
Basic Arabic Phrases and Numbers
Knowing some Arabic words and numbers may help during your vacation in Egypt, particularly if you need immediate any kind of assistance / help.
General Words
| Short | Long | Word |
| Salam | Al-Salamu Alekum | Hello/Goodbye |
| Sabah EL-Kheir | Good Morning | |
| Masa EL-Kheir | Good Evening | |
| Aiwah | Yes | |
| Laa | No | |
| Mesh | Not | |
| Min Fdlak | Please (m) | |
| Min Fadlik | Please (f) | |
| Min Fadlikom | Please (p) | |
| La ataklam Araby | I don’t speak Arabic | |
| Tamam | Alright | |
| Kewayyes | Good | |
| Wehesh | Bad | |
| Keteer | Much | |
| Awy | Much | |
| Ghaalee | Expensive | |
| Teeiil / Thekel | Heavy (weight) | |
| Khafif | Light (weight) | |
| Taweel | Long (dist) | |
| Aaly | High | |
| Kasiir / Ossayyar | Short (dist) | |
| Gedeed | New | |
| Kadeem/Adeem | Old | |
| Lateef | Nice |
Emergency
| Short | Long | Word |
| /OR Agzakhana | Saydalliyyah | Pharmacy |
| Dawaah | Medicine | |
| Mostashfah | Hospital | |
| Mosaadaah | Help (n) | |
| Saaidni (to m) | Help me | |
| Saadiny (to f) | Help me | |
| IL-Polees/IL-Shortah | Police | |
| Essaaf | Ambulance |
Colours
| Short | Long | Word |
| Abyyad | White | |
| Eswid | Black | |
| Akhdar | Green | |
| Azrak | Blue | |
| Ahmar | Red | |
| Asfar | Yellow | |
| Bonni | Brown |
Directions
| Short | Long | Word |
| Yemeen | Right | |
| Yasar/Shimal | Left | |
| Amam | (in) Front | |
| Khalf/Wara | Behind | |
| Aiyn/Feen | Where | |
| Hona/Hena | Here | |
| Honak/Henak | There | |
| AAla/Fouk | Over/Above | |
| Asfal/That | Under/Below | |
| Biganeb/ganb | Beside/By |
Money
| Short | Long | Word |
| Bank | Bank | |
| Taghier Omla | (to) Change | |
| Afok Omla (I) | Change (V) | |
| Fakkah | Change (N) | |
| Noss | Half | |
| Feloos | Money | |
| Geneh | Pound |
Days of the week
| Short | Long | Word |
| AL-Sabt | Saturday | |
| AL-Ahad/AL-Had | Sunday | |
| AL-Etneen | Monday | |
| AL-Talat | AL-Tholathaa/ | Tuesday |
| AL-Arbaa | Wednesday | |
| AL-Khamees | Thursday | |
| AL-Gomaa | Friday |
Time/days/months/seasons
| Short | Long | Word |
| Youm | Day | |
| /OR EL-Naharda | AL-Youm | Today |
| /OR Embarih | Ams | Yesterday |
| /OR Bokra | Ghadan | Tomorrow |
| Osboua | Week | |
| Shahr | Month | |
| /OR Sana | Aam | Year |
| /OR badry | Mobakker | Early |
| /OR Metaakhar | Motaakhir | Late |
| /OR AL-Sobh | AL-Sabah | Morning |
| /OR AL-Dhohr | AL-Dhaheera | Noon |
| AL-Asr | Baad EL-Dhor | Afternoon |
| AL-Maghreb | Sunset | |
| /OR EL-Leil | AL-Massa | Evening |
| EL-Fagr | Dawn | |
| EL-Kharif | Autumn | |
| EL-Shetaa | Winter | |
| EL-Rabea | Spring | |
| EL-SAIF | Summer | |
| Bard | Cold | |
| Harr | Hot |
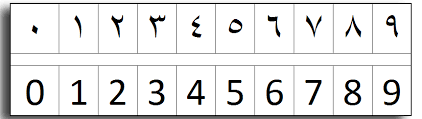
Numbers
| Word | In Arabic | Number |
| wahid | 1 | 1 |
| Etnin/Etneen | 2 | 2 |
| Thalatha/Talata | 3 | 3 |
| Arbaa | 4 | 4 |
| Khamsa | 5 | 5 |
| setta | 6 | 6 |
| Sabaa | 7 | 7 |
| Tamaniya | 8 | 8 |
| Tesaa | 9 | 9 |
| Asharaa | 10 | 10 |
| Hedashar | 11 | 11 |
| Etnashar | 12 | 12 |
| Talatashar | 13 | 13 |
| Arbaatashar | 14 | 14 |
| Khamastashar | 15 | 15 |
| Settashar | 16 | 16 |
| Sabaatashar | 17 | 17 |
| Tamantashar | 18 | 18 |
| Tesaatashar | 19 | 19 |
| Eishreen | 20 | 20 |
| Wahid-we-Eishreen | 21 | 21 |
| Etneen-we-Eishreen | 22 | 22 |
| Talateen | 30 | 30 |
| Wahid-we-Talateen | 31 | 31 |
| Arbieen | 40 | 40 |
| Wahid-we-Arbieen | 41 | 41 |
| Khamseen | 50 | 50 |
| settieen | 60 | 60 |
| Sabieen | 70 | 70 |
| Tamaneen | 80 | 80 |
| Tessieen | 90 | 90 |
| Miyyaa | 100 | 100 |
| Miyyaa-we-Wahid | 101 | 101 |
| Miyyaa-we-Etneen | 102 | 102 |
| Miyyaa-we-Aashara | 110 | 110 |
| Meitain | 200 | 200 |
| Meitain-we-Wahid | 201 | 201 |
| Toltomiyyaa | 300 | 300 |
| Robboamiyyaa | 400 | 400 |
| Khomsomiyyaa | 500 | 500 |
| Sottomiyyaa | 600 | 600 |
| Soboamiyyaa | 700 | 700 |
| Tomnomiyyaa | 800 | 800 |
| Tosoamiyyaa | 900 | 900 |
| Alf | 1000 | 1000 |
| Alf-we-Wahid | 1001 | 1001 |
| Alfien | 2000 | 2000 |
| Talatalaaf | 3000 | 3000 |
| Arbaatalaaf | 4000 | 4000 |
| Khamastalaaf | 5000 | 5000 |
| Settatalaaf | 6000 | 6000 |
| Sabaatalaaf | 7000 | 7000 |
| Tamantalaaf | 8000 | 8000 |
| Tesaatalaaf | 9000 | 9000 |
| Aashartalaaf | 10000 | 10000 |
Travel/Roads/shopping/Means of Transportation
| Short | Long | Word |
| Tayyarah | Aeroplane / Craft | |
| Mattaar | Airport | |
| Mahattet EL-Kettaar | Railway Station | |
| Kettaar | Train | |
| Autobees | Bus | |
| Meenah | Port/Harbour | |
| Shareia | Street | |
| Tareek | Avenue | |
| Midaan | Square | |
| Kobrii | Bridge | |
| Tazkarah | Ticket | |
| IL-Mawaeed | Timetable | |
| Saaiiq / Sawwaq | Driver | |
| Morsheed (Siyahi) | Guide (tour) | |
| Bisoraa | Hurry | |
| Besheesh | Slowly (adv) | |
| Entazer/Estannah | Wait (v) | |
| Hadeeka/Geninah | Garden/park | |
| Boheirah | Lake | |
| Gabal | Mountain | |
| Keneissah | Church | |
| Masjed / Gaameia | Mosque | |
| Mathaf | Museum | |
| Maabaad | Temple | |
| Seffaraa | Embassy | |
| Konsoliyyah | Consulate | |
| Wezarah | Ministry | |
| Souq | Market | |
| Dahhab | Gold | |
| Faddah | Silver | |
| Khatim | Ring | |
| Selselah | Necklace | |
| Eswerah/Gheweishah | Bracelet | |
| Eisharp | Scarf | |
| Kamiis / Amiis | Shirt | |
| Gazmah (s&p) | Shoes | |
| Hareer | Silk | |
| Souf | Wool | |
| Ma’aas | Size | |
| Maagoun | Paste | |
| Maagoun senan | Tooth-paste | |
| Kream hela’aa | Shaving cream | |
| Sharab / Sharabat (p) | socks |
Hotel/Resort/Restaurant/food/beverages
| Short | Long | Word |
| Fondok | Hotel | |
| Montagaa | Resort | |
| Mataam | Restaurant | |
| Hammam | Bath/Toilette | |
| Serir | Bed | |
| Ghorfa/Oudaa | Room | |
| Moftaah | Key | |
| Korsii | Chair | |
| Tarabeeza | Table | |
| Lambbah | Lamp | |
| EL-Nour | Light (the) | |
| Hanfiyyaa | Tap | |
| Dosh | Shower | |
| Efttaah | Open (v) | |
| Maftouh | Open (adj) | |
| Ekfel / Eghlek | Close (v) | |
| Makfoul/Moghlaq | Close (adj) | |
| Foutaa | Towel | |
| Nafeza / Shibbak | Window | |
| Baab | Door | |
| Maslouk/Masloua | Boiled | |
| Maakli / Maalii | Fried | |
| Mashwii | Grilled | |
| Mestewi | Well – done | |
| Noss-Sewaa | Medium | |
| Sewaa-Khafif | Rare | |
| Fottour / Eftaar | Breakfast | |
| Ghadaa | Lunch | |
| Aashaa | Dinner | |
| Mafrash | Cover/tablecloth (n) | |
| Shoukaa | Fork | |
| Maalaqah | Spoon | |
| Sekkin/Sekkinah | Knife | |
| Kobbaiyyah | Glass | |
| Tabaq/Tabbaa | Plate/Dish | |
| Zogaga/Ezaza | Bottle | |
| Ezazet Maayiyyah | Bottle (M.Water) | |
| Malh | Salt | |
| Felfel | Pepper | |
| Khaal | Vinegar | |
| Salsa | Sauce | |
| Salatah | Salad | |
| Aiesh | Bread | |
| Zebdah | Butter | |
| Beidaah/Beidd | Egg (s) | |
| Merrabbah | Jam | |
| Lahma | Meat | |
| Feraakh | Chicken | |
| Samak | Fish | |
| Gambari | Shrimps | |
| Roz | Rice | |
| Makaroona | Pasta/Macaroni | |
| Khodaar | Vegetables | |
| Helw / EL-Helw | Dessert | |
| Fakha | Fruit | |
| Maiyyaah | Water | |
| Beiraa | Beer | |
| Neibeez/Neibeet | Wine | |
| Shaii | Tea | |
| Sukkar | Sugar | |
| Kahwa / Ahwa | Coffee (drink) | |
| Kahwa / Ahwa | Coffee-shop/Café | |
| Labban / Haleeb | Milk | |
| Asseer | Juice | |
| /OR Asseer Boroaan | Asseer Botokal | Orange Juice |
| Neinaa | Mint | |
| Shaii bil Neinaa | Mint’ Tea | |
| Erfaa | Cinnamon |
Population
With 104.26 million inhabitants, Egypt is the most populous country in the Arab world and the third in Africa. For decades, the population has been growing by about 2% and more every year. Only the years from 1994 to 2010 under the reign of Husni Mubarak and the year 2017 were below the 2% mark. In international comparison, this growth is considerably above average. Within only 40 years the population has doubled. The Egyptian government sees the continuing high birth rate in particular as a massive economic problem. Similar to China, but not with the reprisals there, Egypt has been trying to implement a “2-child policy” for years. After the turn of the millennium, this strategy was initially successful and the birth rate (number of children per woman) dropped to 2.5.
Population growth in Egypt
From 1960 to 2021 the population of Egypt increased from 26.63 million to 104.26 million people. This is a growth by 291.5 percent in 61 years. The highest increase in Egypt was recorded in 1961 with 2.75%. The smallest increase occurs in 2007 with 1.77%.
N.B:
Egypt’s population is expected to double by 2078
Birth – and death rate in Egypt
Population growth is the result of the birth rate, the mortality rate and the migration rate, for example the year 2020, the population in Egypt increased by about 1,946,000 inhabitants. In the same year, the death rate was 5.7 per 1000 people (~ 577,000 deaths) and the birth rate was 25.1 per 1000 people (2,517,000 births).
Around 43% of the inhabitants live in the country’s larger cities. This growing trend of urbanization is increasing by 2.0% annually.
Largest Cities in Egypt
After Nigeria and Ethiopia, Egypt is the most populated country on the African continent. A majority of the population lives near the banks of the Nile River, which amasses an area of 40,000 square kilometers. This area is the only arable land found in the country. The three largest cities of the country are Cairo, Alexandria, and Giza.
World City Populations 2022
- Tokyo (Population: 37,435,191)
- Delhi (Population: 29,399,141)
- Shanghai (Population: 26,317,104)
- Sao Paulo (Population: 21,846,507)
- Mexico City (Population: 21,671,908)
- Cairo (Greater Cairo) (Population: 20,484,965)
Source:
World population review.
World Data
Economy
Egypt, The meeting point of East and West, occupying nearly one million SQ.KM at the northeast corner of the African continent, mostly desert, except for the Nile Valley and Delta, which denote where most economic activity takes place. Egypt’s economy in reality is highly developed, powered and mostly dependent on agriculture that takes place in the Nile Valley and Nile Delta. Egypt modern economy is traced back to the beginning of the nineteenth century, when Mohamed Ali began the country’s modernization plan, but effectively the two turning points of the economy were , the first following the completion of the Suez Canal in 1869, making Egypt one of the most important world transportation hubs, the second is the completion of the Aswan High Dam in 1971. But due to the rapidly growing population (which is the third in Africa and the largest in the Arab World), it limited the arable land, since 1952 almost all governments had to struggle to meet the demands of such growing population through economic reform and massive investment in all sectors, particularly physical infrastructure.
Economy Basic Facts
| Labor force: | 21.34 million (estimated 2018) |
| Labor force – by occupation: | agriculture 32%, industry 17%, services 51% (estimated 2018) |
| Unemployment: | 9.5% (estimated 2018) |
| Industries: | textiles, food processing, tourism, chemicals, hydrocarbons, construction, cement, metals |
| Agriculture: | cotton, rice, corn, wheat, beans, fruits, vegetables; cattle, water buffalo, sheep, goats |
| Exports: | crude oil and petroleum products, cotton, textiles, metal products, chemicals |
| Export partners: | US 13.4%, Italy 9.6%, Spain 7.8%, Syria 6%, France 4.9%, Germany 4.9%, UK 4.5% |
| Imports: | machinery and manufacturing equipment, foodstuffs, chemicals, wood products, fuels |
| Import partners: | US 10.8%, Germany 7.3%, China 6.6%, France 6.4%, Italy 5.9%, Saudi Arabia 4.5% |
| Currency: | Egyptian pound (EGP) |
N.B
The tourism business employs around 13% of Egypt’s workforce.
With Egypt’s sovereignty over the Suez Canal, it is possible to reach the Indian Ocean from the Mediterranean Sea (Annual Revenue this year 2022 exceeded 7 Billion US$D “in result of the opening the new Canal (a new branch, makes possible, navigating both ways).
More than a third of Egypt’s workforce is engaged in agriculture.
Income Source
Egypt economy relies mainly on agriculture, petroleum, natural gas, imports, media and tourism.
Petroleum
Despite the fact that, Egypt is not a member of OPEC, but it is an important energy producer (of non OPEC Members), it is ranked the sixth-largest oil-reserved country in Africa,
History of oil discovery in Egypt goes back to the beginning of the twentieth century, when unbelievable finds took place in the Gulf of Suez, followed by more discoveries in the peninsula of Sinai, western and eastern deserts, in frank word, these are the most remarkable sites of oil fields and production throughout the country, in addition to some others.
In the beginning of the millennia, it was estimated that Egypt’s oil reserves stand at 3.7 bbl (Billion Barrel) of which not less than 2.9 bbl crude. Nearly 50% of Egypt’s oil production comes the area of the Suez Gulf, while the other sites in the western desert, the eastern desert and Sinai Peninsula provide the remaining 50%.
Natural Gas
Despite the world-great attention given to green energy, Natural Gas remains a very important energy source. Egypt is classified as one of the major players in Natural Gas Production, with natural gas reserves exceeding (66 Trillion Cubic Feet). The importance of such energy source increased with the discovery of more deposits in the Nile Delta, increasing the country’s reserves. But 2015 was a happy years for Natural Gas Reserves in Egypt with the discovery of “Zohr” natural gas field.
Egypt prides of having the largest natural gas field ever found in the Mediterranean, the”Zohr” natural gas field. The field was discovered in 2015 by “ENI” ( an Italian Energy Company), the field began producing its gas a couple of years ago, and as estimated, its reserves exceeds over 850 billion cubic meters. Natural Gas which is exported to some Middle Eastern countries, including Jordan, is expected shortly to be exported to Europe.
Agriculture
Egypt has always been identified as the “gift of the Nile” as “Herodotus” said. The land which the Greeks in their early days exclaimed, seldom rain but green, thanks to the mighty river Nile which waters the land by the annual flood, and silt deposited on its banks and Delta through millennia. Wheat and other grains thrive during the winter (but dramatically the land fed the ancient world with its wheat “the granary of the world then” has to import it due to the increasing population, while its cultivation became limited due to many reasons), flax and sugar in the spring, fruits (mainly in summer-but nowadays all year round), flowers, rice and corn in autumn. But Egypt’s agricultural wealth is due not only to nature’s provision; man’s efforts to irrigate such cultivated land make Egypt as much as gift of man (Fellahin-Farmers) as of the Nile. Historians have suggested that agriculture began in Egypt some 7000-8000 years ago. By 5000 BC, the Egyptians were developing the techniques of irrigation, ploughing, harvesting and storing the grain. The abundance of food which resulted later enabled some to concentrate on metal-working and other skills, thus laying the foundations of a new great civilization.
In pre-dynastic period around 4500 BC, the Egyptians were already domesticating fowl, especially geese. The Egyptians were also among the first people to domesticate animals and use them as beasts of burden, mainly in conjunction with that invention revolutionized agriculture “the plough”.by early dynastic period (some 5000 years ago), the Egyptian farmers had developed the Shadouf (a device with weighed lever which enabled them to raise water from the river into canals. The introduction of the Saqqiah/waterwheel (drawn by oxen-donkey) by the Greek period made it possible to bring appreciable amounts of water to cultivate higher lands , helped in the development of irrigation resulting vast areas to be reclaimed and cultivated. Though agriculture is relatively simple and rewarding in the Nile Valley, the Egyptian farmer had to work hard in ancient times, as h still has, modern technology shared in the change a bit in agriculture, as the ox-driven plough has been largely replaced by modern tractors, but Egypt’ Agricultural scenes painted on Pharaonic tombs’ walls, could be seen live, today in the millions of fields of agriculture everywhere in Egypt, as style-change in rural society is rarely happened here. It’s a concept inherited thousands of years past. However, it was only after the completion of the Aswan High Dam in 1971 that it became possible to reclaim from the desert/ without neglecting the benefits of these desert-wells dug to provide more reclaimed land (like what we see particularly in Bahariyaa / Siwa and Dakhla Oases) from the desert gigantic tracts of land. No one denies the efforts made by different governments since 1954, among which are co-operatives (a sort of organizations) were setup providing farmers with production services, modern equipment and marketing and technical expertise.
Statistics – source / Ref: World Fact page.